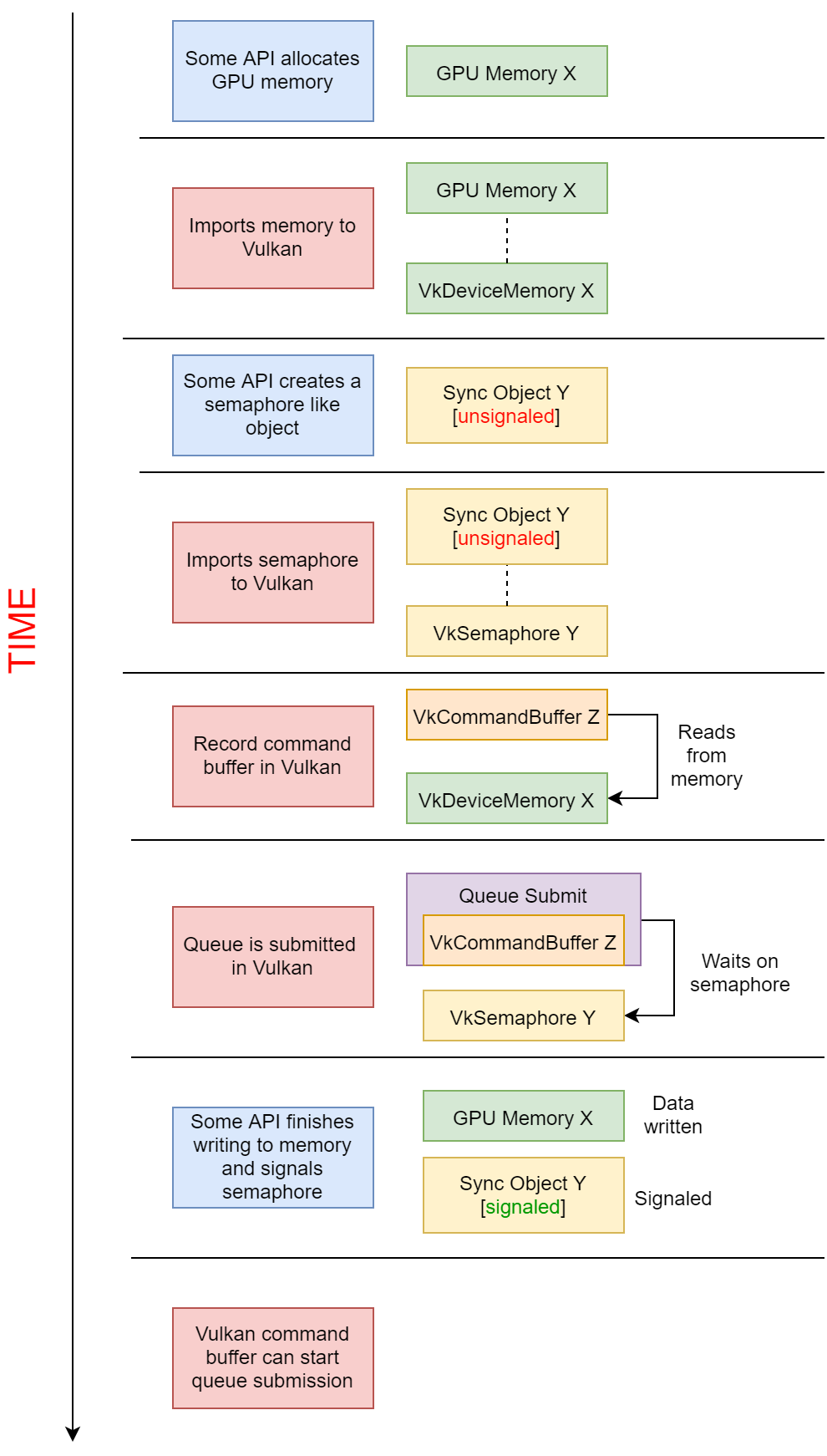
External Memory and Synchronization
Sometimes not everything an application does related to the GPU is done in Vulkan. There are various situations where memory is written or read outside the scope of Vulkan. To support these use cases a set of external memory and synchronization functions was created
Extension breakdown
While there may seem to be a lot of VK_KHR_external_* extensions, they are in practice, just nicely separating the logic apart.
Memory vs Synchronization

There is a set of extensions to handle the importing/exporting of just the memory itself. The other set extensions are for the synchronization primitives (VkFence and VkSemaphore) used to control internal Vulkan commands. It is common practice that for each piece of memory imported/exported there is also a matching fence/semaphore to manage the memory access.
Handle Types

Depending on the platform there will be a specific handle used to communicate between Vulkan and the external platform. For example, POSIX fd are used for most non-Windows based platforms.
Capabilities
The VK_KHR_external_fence_capabilities, VK_KHR_external_semaphore_capabilities, and VK_KHR_external_memory_capabilities are simply just ways to query information about what external support an implementation provides.
External Memory
The VK_KHR_external_memory extension is mainly to provide the VkExternalMemoryHandleTypeFlagBits enum which describes the type of memory being used externally.
There are currently 3 supported ways to import/export memory
-
VK_KHR_external_memory_fdfor memory in a POSIX file descriptor -
VK_KHR_external_memory_win32for memory in a Windows handle -
VK_ANDROID_external_memory_android_hardware_bufferfor memory in a AHardwareBuffer
Each of these methods has their own detailed descriptions about limitations, requirements, ownership, etc.
Importing Memory
To import memory, there is a VkImport*Info struct provided by the given external memory extension. This is passed into vkAllocateMemory where Vulkan will now have a VkDeviceMemory handle that maps to the imported memory.
// some external memory types require dedicated allocation
VkMemoryDedicatedAllocateInfo dedicated_info;
dedicated_info.buffer = buffer;
VkImportMemoryFdInfoKHR import_info;
import_info.pNext = &dedicated_info;
import_info.handleType = VK_EXTERNAL_MEMORY_HANDLE_TYPE_OPAQUE_FD_BIT;
import_info.fd = fd;
VkMemoryAllocateInfo allocate_info;
allocate_info.pNext = &import_info
VkDeviceMemory device_memory;
vkAllocateMemory(device, &allocate_info, nullptr, device_memory);Exporting Memory
To export memory, there is a VkGetMemory* function provided by the given external memory extension. This function will take in a VkDeviceMemory handle and then map that to the extension exposed object.
VkExportMemoryAllocateInfo export_info;
export_info.handleTypes = VK_EXTERNAL_MEMORY_HANDLE_TYPE_OPAQUE_FD_BIT;
VkMemoryAllocateInfo allocate_info;
allocate_info.pNext = &export_info
VkDeviceMemory device_memory;
vkAllocateMemory(device, &allocate_info, nullptr, device_memory);
VkMemoryGetFdInfoKHR get_handle_info;
get_handle_info.memory = device_memory;
get_handle_info.handleType = VK_EXTERNAL_MEMORY_HANDLE_TYPE_OPAQUE_FD_BIT;
int fd;
vkGetMemoryFdKHR(device, &get_handle_info, &fd);Synchronization
External synchronization can be used in Vulkan for both VkFence and VkSemaphores. There is almost no difference between the two with regards to how it is used to import and export them.
The VK_KHR_external_fence and VK_KHR_external_semaphore extension both expose a Vk*ImportFlagBits enum and VkExport*CreateInfo struct to describe the type a synchronization being imported/exported.
There are currently 2 supported ways to import/export synchronization
-
VK_KHR_external_fence_fd/VK_KHR_external_semaphore_fd -
VK_KHR_external_fence_win32/VK_KHR_external_semaphore_win32
Each extension explains how it manages ownership of the synchronization primitives.